Common Types of Water Filters
Water is the basic human need essential for the survival and healthy life. In the modern era, pollution has affected our lives in many ways, and we bring different types of water filters to purify the water. It has become really difficult to get pure and clean water; boiling the water is not enough.
In addition, we need a purification system to clean our water from all the impurities and added metals to make it healthy and drinkable without causing any significant damage to our health and body. There are multiple methods to clean water and purify it.

Moreover, all these have got some practical difficulties, their own benefits, and some drawbacks as well. That can be sorted out on the local level. You can decide about the filtration method according to the type of water supply, piping system, contaminants in the water, and most importantly, your budget.
Here are multiple types of water filters, their specific properties, and some pros and cons to help you decide the better one
Common Types of Water Filters How They Work
1. Sediment Filtration
This is a mechanical method of water filtration. It removes all the solid particles, including dust, rust, debris, and even tiny bacteria, through the process of filtration. Further, it consists of the mesh made up of polypropylene in most cases, and the size of the pores of this mesh determines the strength of the filtration and water flow rate.

Additionally, the size of the pore ranges from 1 micron to 100 microns. The smaller the pore size, the more effective filtration occurs. It removes minor impurities from the water. The mesh, which has a porous size of 0.5 microns, can filter microscopic cysts of some organisms and make water purest and healthier.
Moreover, sediment filtration is an important step in many industrial filtration processes to increase the membrane life of other filtration methods.
Pros
Cons
2. Activated Carbon Filtration
These carbon filters are porous and positively charged. It absorbs the contaminants effectively due to the porous surface. Further, a positive charge on these particles helps to remove negatively charged chlorine, chloramine, and volatile organic compounds. In addition, it can reduce bacterial growth and removes bacterial cysts from the drinking water.
Moreover, it helps to improve the taste and smell of the drinking water. It purifies the drinking water and improves its quality as well. The large porous surface provides a large surface area and helps remove any impurities from the water through adsorption.
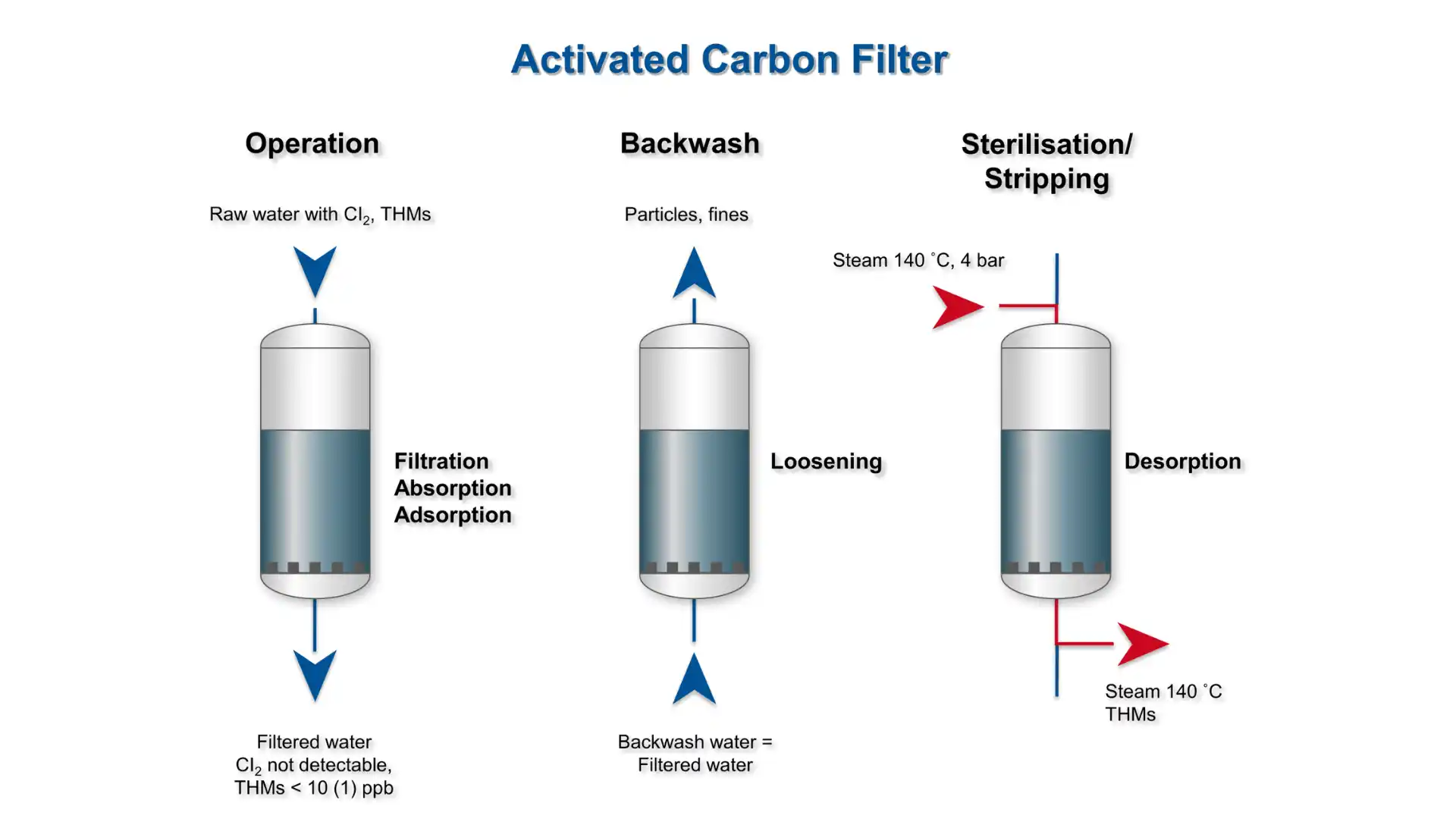
Further, activated carbon is found in two forms in the filtration process, i.e. carbon block and activated granulated carbon. This carbon block or granulated carbon can be used in many prefiltration systems in housing filtration systems or different industries.
Pros
Cons
3. Activated Alumina Filtration
This filtration system is made of Aluminium oxide ( Bauxite).
A highly porous and absorptive material to purify water from Flourine, Thallium, Selenium Arsenic.
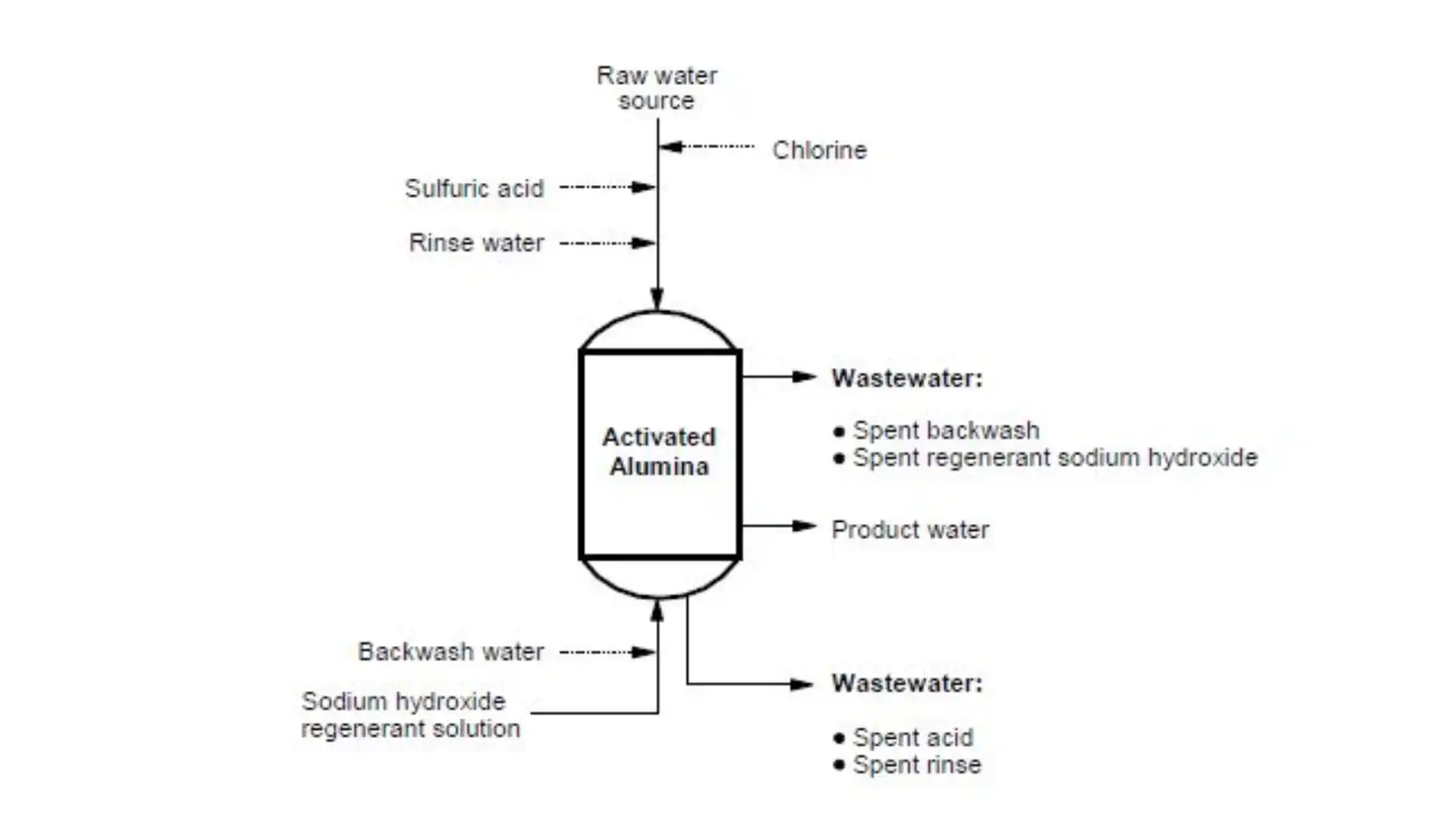
Furthermore, this filtration method is more useful in households where fluoridated water is supplied or the areas where water has high arsenic content.
Pros
Cons
4. Ion Exchange Method
The ion exchange method is mainly used in areas where hard water is the main problem. It makes washing and bathing difficult. Plus, in many filtration systems, the double ion exchange system uses anionic and cationic exchanges separately to remove undesired cations and anions from water.
Further, a beaded resin present removes the undesirable substance from the water running through it by a chemical reaction. In anionic exchange, negatively charged fluorine, Arsenic, and nitrate exchanges with the desirable ions like chlorine.
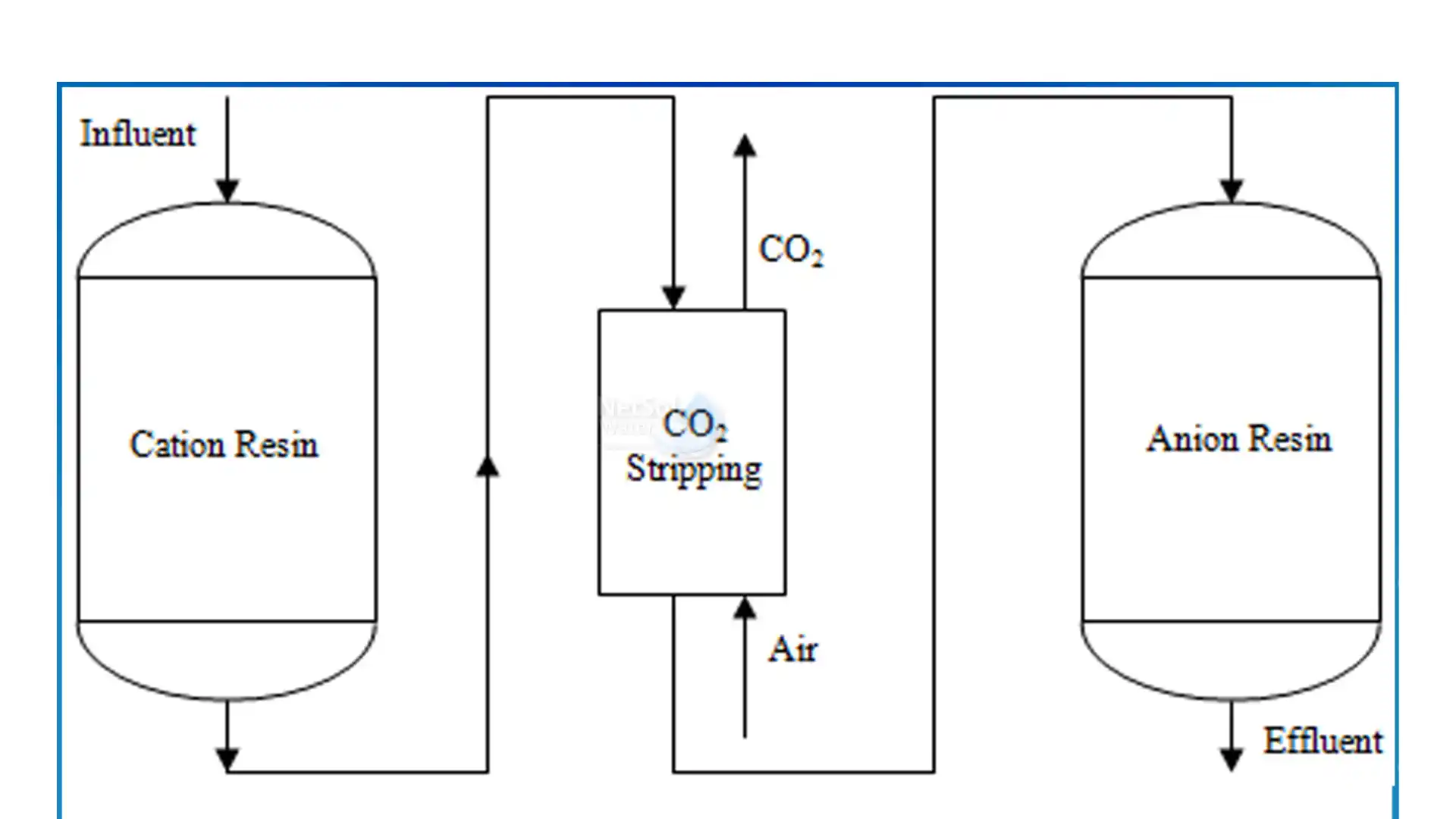
On the other hand, magnesium and calcium are exchanged with sodium or hydrogen, and among these, hydrogen is preferred because additional sodium in water causes increased cardiovascular disease risks.
Moreover, when ion exchange resin is fully used, it can be regenerated by adding brine (sodium chloride solution) or hydrochloric acid in it.
Pros
Cons
5. Water Distillation
This is the most natural form of purification of water. It implies the method of boiling, evaporation, and condensation. This process is slower however provides the purest form of water free of all kinds of contaminants. It can filter calcium, magnesium, fluorine, chlorine, nitrates, and organic contaminants left behind during the process of boiling and discarded.
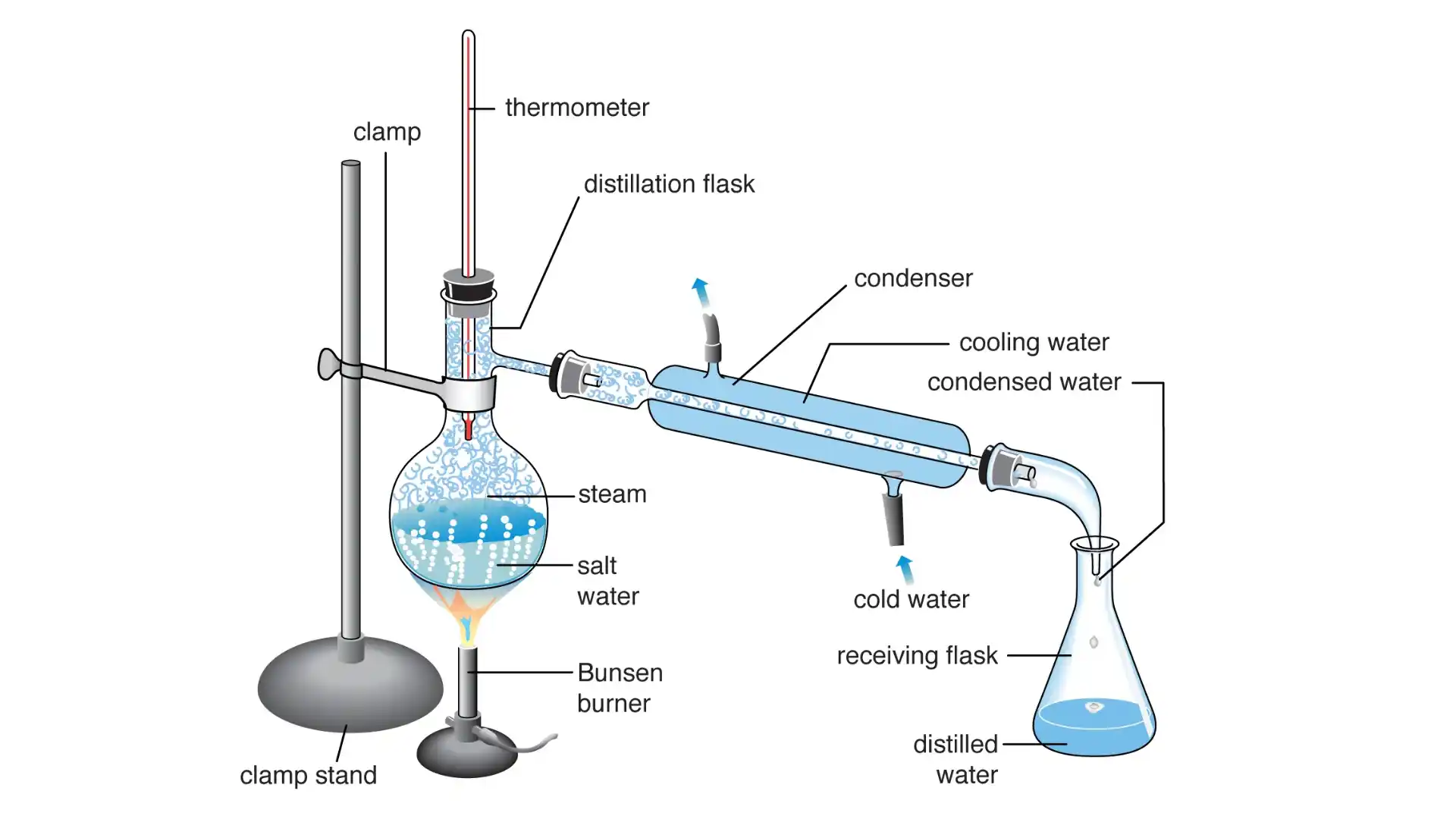
However, leaving behind the volatile compounds that vaporize with water. This costly and time-consuming process is mostly used at the industrial level.
Pros
Cons
6. Reverse Osmosis Filtration
This filtration method implies a semipermeable membrane that removes all the contaminants from the solvent (water). It cleans the impurities and makes it pure as a safe drinking option. Usually, the osmosis removes the solvent from the solute; however, the solute is removed from the solvent; that’s why reverse osmosis takes place.
Furthermore, the membrane is usually polypropylene material with a size up to 0.0001 microns. It enables it to separate all organic and most inorganic compounds, bacterial products, viruses, and minerals from water.
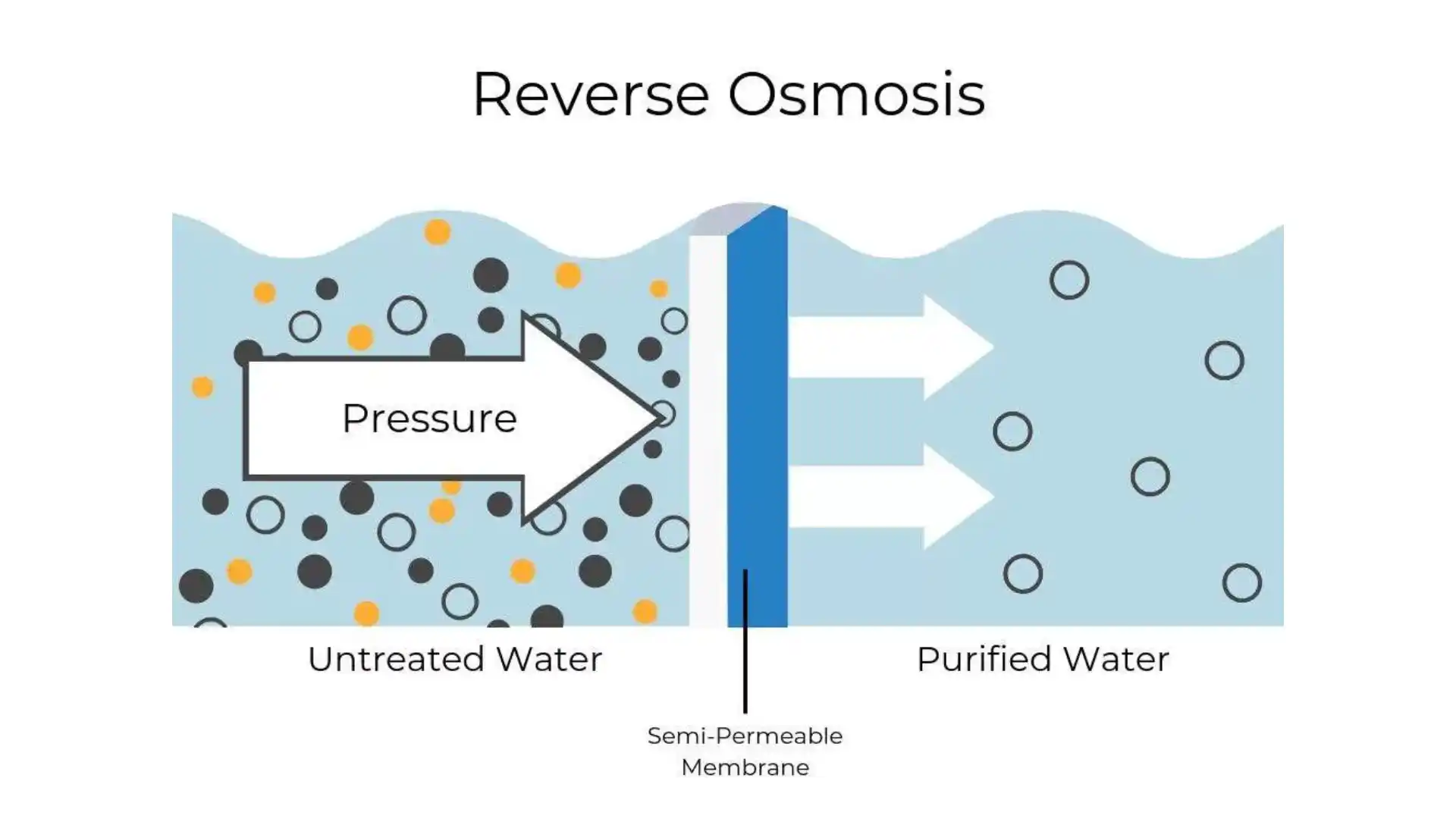
There is a large amount of wastewater in the form of brine that comes with product water almost in ratio 3:1. There is a risk of damage to the filtration membrane by chlorine. So a pre-filtration system of activated carbon is always needed with the reverse osmosis system.
Pros
Cons
7. Ultrafiltration
This filtration process works with the help of hydrostatic pressure to force water to pass through a semipermeable membrane. Further, it allows removing most of the contaminants from the water through the 0.01 microns to 0.05 microns hollow fibers. This membrane filtration method can not remove dissolved solids from the water. On the other hand, it is very sensitive to chlorinated water and purifies it efficiently.
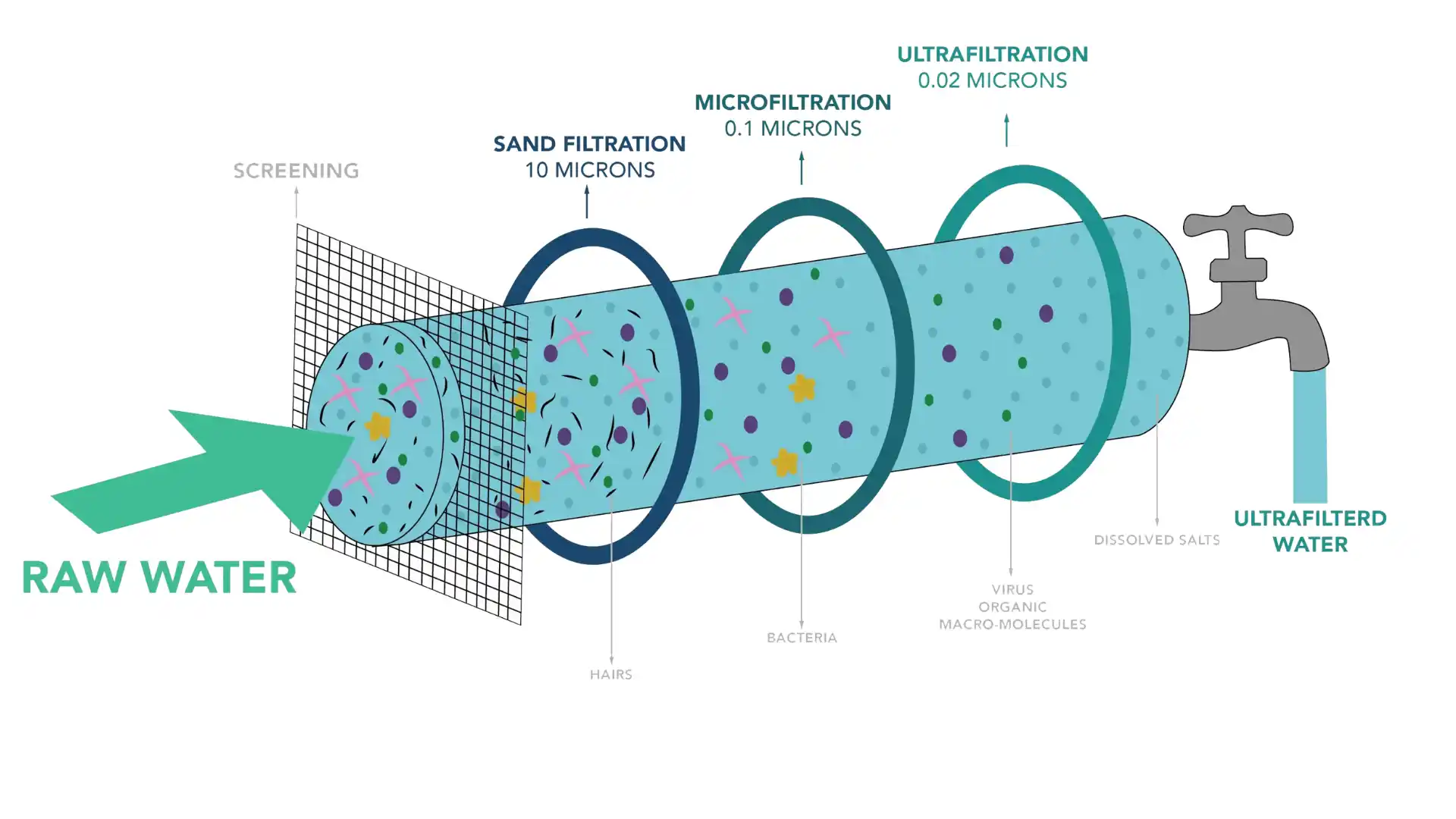
Plus, the membranes with smaller hollow fibers can filter bacterial products and viruses from water. This method is preferred by industrial filtration plants and wastewater recycling plants.
Pros
Cons
8. Ultraviolet Disinfection
This method uses ultraviolet light rays to disinfect water and kill bacteria and viruses present in the water without any harmful effect. This method doesn’t disturb the natural odor and taste of the drinking water. Moreover, it doesn’t need any additional chemicals to do the job.

However, water filtration is necessary with this method of purification to remove the additional contaminants.
Pros
Cons





